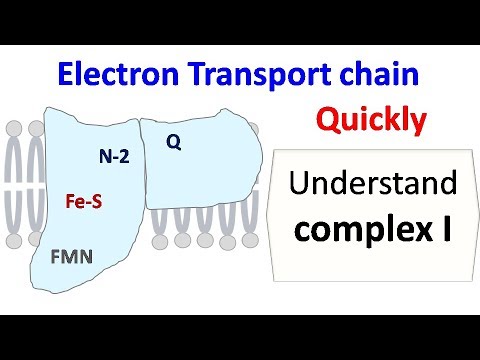
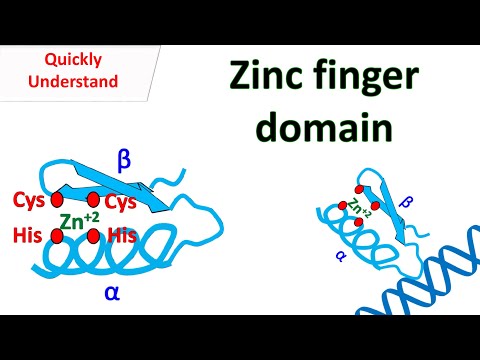
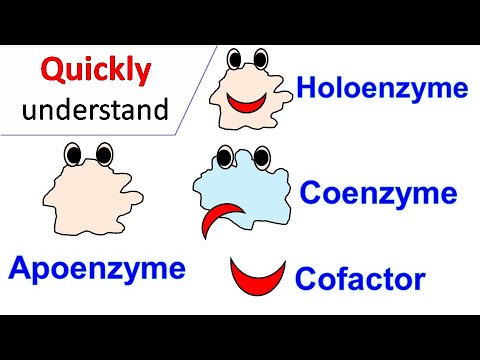
Quick Biochemistry Basics | Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) @quickbiochemistrybasics | Uploaded 6 years ago | Updated 12 hours ago
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique used in molecular biology for DNA amplification of a segment of DNA across several orders of magnitude, generating thousands to millions of copies of a particular DNA sequence. Almost all PCR applications employ a heat-stable DNA polymerase, such as Taq polymerase, an enzyme originally isolated from the thermophilic bacterium Thermus aquaticus. This DNA polymerase enzymatically assembles a new DNA strand from free nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA, by using single-stranded DNA as a template and DNA oligonucleotides (the primers mentioned above) to initiate DNA synthesis.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique used in molecular biology for DNA amplification of a segment of DNA across several orders of magnitude, generating thousands to millions of copies of a particular DNA sequence. Almost all PCR applications employ a heat-stable DNA polymerase, such as Taq polymerase, an enzyme originally isolated from the thermophilic bacterium Thermus aquaticus. This DNA polymerase enzymatically assembles a new DNA strand from free nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA, by using single-stranded DNA as a template and DNA oligonucleotides (the primers mentioned above) to initiate DNA synthesis.